Conductors, insulators and Semiconductors
Conductors, insulators and Semiconductors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Intrinsic Semiconductor, Intrinsic Carrier Concentration, Effect of Temperature on Electrical Conductivity of Intrinsic Semiconductors & Effect of Temperature on Intrinsic Charge Carrier Density etc.
Important Questions on Conductors, insulators and Semiconductors
The filament of electric bulb is generally made of tungsten because
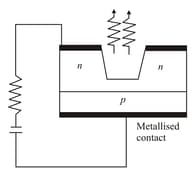
The diagram below is showing:
What will happen if we increase temperature in an intrinsic semiconductor ?
In an intrinsic semiconductor, Its carrier density increases with _____.
In an intrinsic semiconductor, Its carrier density increases with temperature.
An intrinsic semiconductor has the following properties:
1. Its electron concentration equals its hole concentration.
2. Its carrier density increases with temperature.
3. Its conductivity decreases with temperature.
No crystal is found to be prefect at room temperature. The defects present in the crystals can be stoichiometric or non-stoichiometric. Due to nonstoichiometric defects, the formula of the ionic compound is different from the ideal formula. For example, the ideal formula of ferrous oxide should be but actually in one sample, it was found to be . This is because the crystal may have some ferric ions in place of ferrous ions. These defects change the properties of the crystals. In some cases, defects are introduced to have crystals of desired properties as required in the field of electronics. Doping of elements of Group 14 with those of Group 13 or 15 is most common. In ionic compounds, usually impurities are introduced in which the cation has higher valency than the cation of the parent crystal, e.g., into .
Which one of the following doping will produce p-type semiconductor ?
In a pure semiconductor, electric current is due to_________.
In a p–type semiconductor, the concentration of holes is The intrinsic carrier concentration is . The concentration of electrons will be.
Assertion : An n-type semiconductor has a large number of electrons but still it is electrically neutral.
Reason : An n-type semiconductor is obtained by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with a pentavalent impurity.
A semiconductor has equal electron and holes concentration of . On doping with certain impurity, electron concentration becomes . Then the semiconductor is
Electric current in extrinsic semiconductor in respect of mobility is expressed as
Electric current in extrinsic semiconductor is
A silicon specimen is made into a -type semiconductor by doping, on an average, one indium atom per silicon atoms. If the number density of atoms in the silicon specimen is atoms , then the number of acceptor atoms in silicon per cubic centimeter will be
The conductivity of a semiconductor sample having electron concentration of , hole concentration of , electron mobility of and hole mobility of is
(Take charge of an electron as )
If the mobility of electron in an n-type semiconductor is , then determine the density of donor atoms to be added to intrinsic germanium specimen to make it an n-type semiconductor of conductivity
A piece of copper and the other germanium are cooked from room temperature at , then which of the following would be a correct statement?
When the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor is due to the breaking of its covalent bonds, then the semiconductor is said to be
In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true:
The mobility of free electrons is greater than that of free holes because
